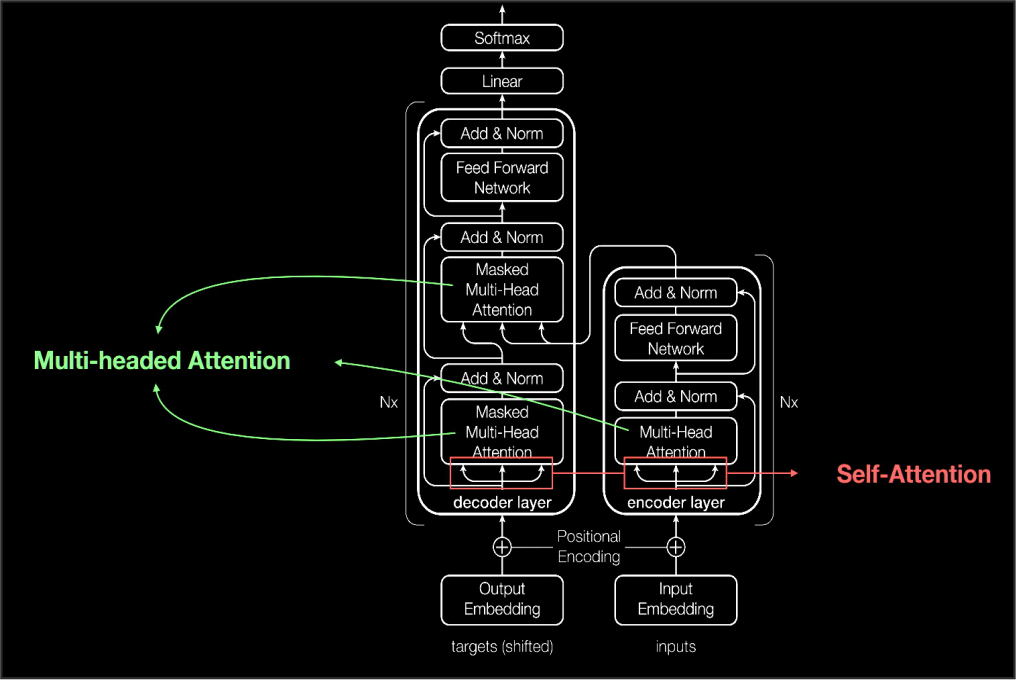
Google’s research team has introduced a novel neural network architecture named “Titans,” designed to address the escalating computational and memory demands of large language models (LLMs). Traditional transformer-based LLMs rely on self-attention mechanisms to process token relationships, which become increasingly resource-intensive as sequence lengths grow, leading to quadratic increases in computation and memory usage.
The Titans architecture innovatively integrates standard attention layers with neural memory modules, effectively distinguishing between short-term and long-term memory processing. This separation allows the model to efficiently manage extensive sequences by storing and recalling pertinent information without the prohibitive costs associated with traditional methods. The neural memory component evaluates the “surprise” factor of data—identifying and retaining information that deviates significantly from existing knowledge, thereby optimizing memory utilization.
By adopting this architecture, Titans can handle sequences comprising millions of tokens, surpassing the performance of conventional LLMs and alternative models like Mamba, all while maintaining a reduced parameter count. This advancement signifies a substantial leap in developing more efficient and scalable LLMs, paving the way for applications that require processing extensive textual data without incurring exorbitant computational costs.
Paper link : https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.00663